Design RNA for the origin of life
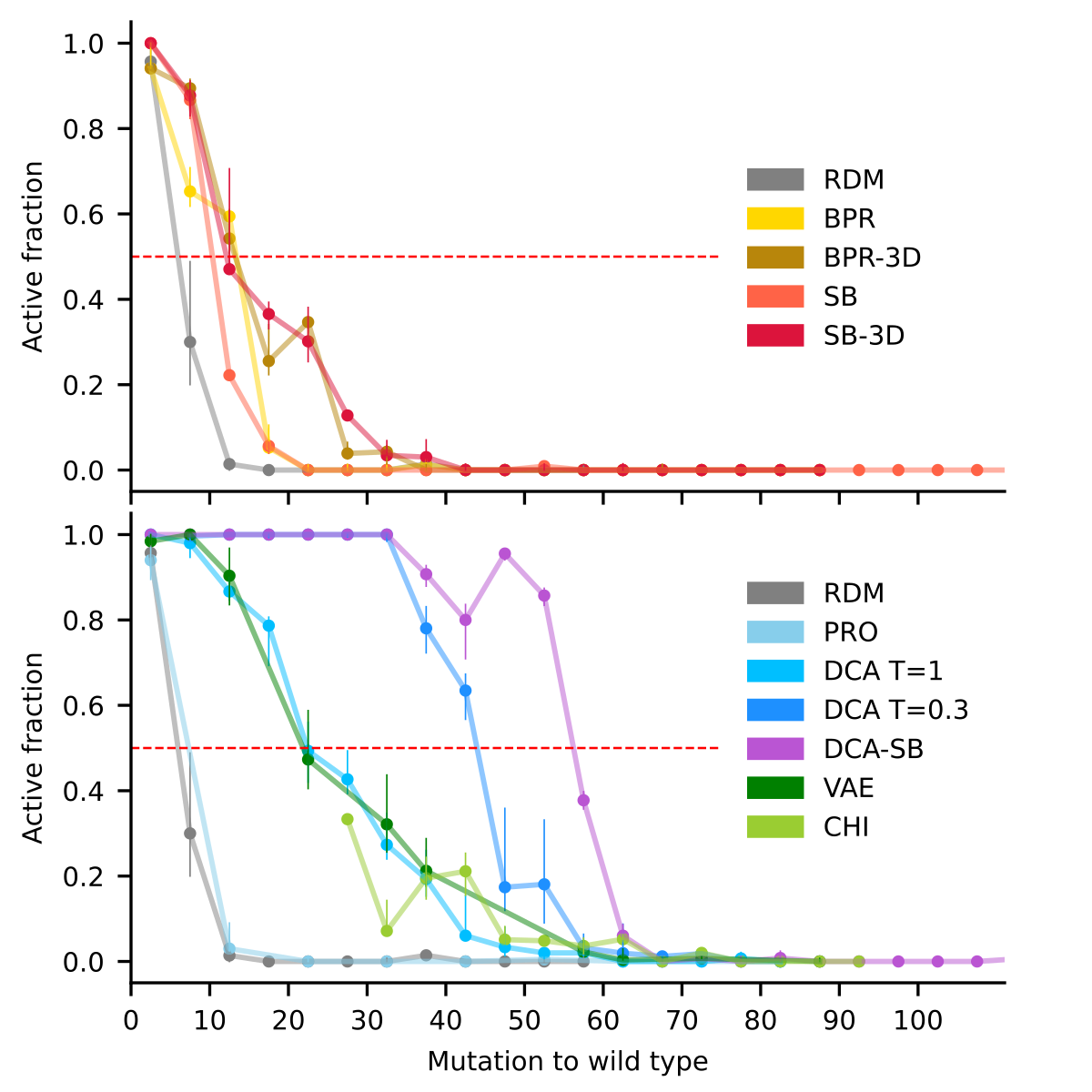
Estimating the plausibility of RNA self-reproduction is central to origin-of-life scenarios but self-reproduction has been shown in only a handful of systems. Here, we populated a vast sequence space of ribozymes using statistical covariation models and secondary structure prediction. Experimentally assayed sequences were found active as far as 65 mutations from a reference natural sequence. The number of potentially generated sequences together with the experimental success rate indicate that at least ∼1039 such ribozymes may exist. Randomly sampled artificial ribozymes exhibited autocatalytic self-reproduction akin to the reference sequence. The combination of high-throughput screening and probabilistic modeling considerably improves our estimation of the number of self-reproducing systems, paving the way for a statistical approach to the origin of life.
